Kuwait
Kuwait
Kuwait’s population was estimated at 4.79 million, including 3.27 million expatriates, in 2023.[1] High immigration rates and heavy dependence on foreign labor have swung the population pyramid of Kuwait in favor of the working-age groups (15 to 64 years), which account for 78.3 percent of the total population.[1] According to the latest data by Kuwait’s Central Statistical Bureau (CSB) in 2022, the total fertility rate is 1.54 children per woman, life expectancy is around 80.7 years, and levels of maternal mortality and infant mortality are around 6.02 per 100,000 and 8.23 per 1,000, respectively.[1] With a government health expenditure at 5.67 percent of GDP, out-of-pocket health expenditure (as a percent of current health expenditure) is at 9.13 percent, the second lowest rate among Arab countries, after Oman.[3]
Kuwait’s Human Development Index value for 2021 is 0.831, which positioned the country among the very high human development group — ranking 50 out of 191 countries and territories and the fifth among Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. The country’s value is below the average of 0.896 for countries in the very high human development group and above the average of 0.708 for countries in the Arab States.[4]
Following the adoption of substantial structural reforms to improve the business environment in 2019, Kuwait made it for the first time in the World Bank’s 2020 Doing Business list of the 10 most improved economies, out of 190 economies. Reforms in Kuwait mainly focused on simplifying the start of a business, digitizing the process to get electricity, facilitating access to credit, streamlining the construction permitting process, improving the quality of its land administration system, protecting minority investors and advancing trading across borders.[5]
The Kuwaiti economy relies heavily on its hydrocarbon resources, with oil constituting almost 90 percent of the country's total government revenues in 2020.[6] In the aftermath of the drop in oil prices in 2014, the authorities announced a series of fiscal and structural reforms to strengthen the role of the private sector, improve the business environment, boost the employment of Kuwaitis, and promote the development of small and medium enterprises (SMEs). However, as oil prices recovered in 2017-2018, public expenditures rose by 8.7 percent, [6] and the implementation of a 5 percent Value-Added Tax (VAT) was postponed to 2021.[7] Closing Account data for FY2019/20 showed a decrease in actual public expenditure by 3.2% compared to the previous year.[6]
Crude oil production rose from 2.704 million barrels per day on average during 2017 to 2.736 million barrels per day in 2018, and the increase in oil prices in 2018 to $69.78 per barrel, up from $52.43 per barrel in the previous year, have resulted in an increase in oil GDP growth from -7.2 percent to 1.3 percent. On the other hand, the non-oil growth decreased to 1.1 percent in 2018 and 1.8 percent in 2017, after reaching 3.6 percent in 2016. [6] Consequently, GDP growth was estimated at 2.4 percent in 2018, up from -4.7 percent in 2017. In 2020, GDP growth contracted to -8.8, the lowest in the last 2 decades then it increased to register 1.14 and 8.8 in 2021 and 2022 consequently.[8]
In 2018, Inflation decelerated for the second year in a row to 0.6 percent, after reaching 1.5 percent in 2017 and 3.5 percent in 2016. This deceleration was a result of the deflation in housing services and the decline in transport costs.[6] From 2019, Inflation rose gradually reaching 3.98.[1]
Driven by lower oil revenues and higher spending, the current account balance narrowed from 14.4 percent of GDP in 2018 to 4.5 percent of GDP in 2020 which then increased to 36 percent in 2022. [8] According to the IMF, net lending/borrowing was estimated at -11.6 percent of GDP which then registered 19 percent of GDP in 2022.[8]
The labour force participation rate decreased from 73 percent in 2019 to 69.9 in 2020 and then increased gradually to 71.5 in 2022. The unemployment rate registered its highest value in 2020 at 3.3 and then decreased gradually reaching 2.4 in 2022. Additionally, women face higher unemployment rate at 3.32 percent, compared to 1.2 percent for men in 2022. The unemployment rate is higher among youth, reaching 15.3 percent, where the gap becomes larger between males and females, with an unemployment rate for young females almost triple that of young males, at 28.9 percent compared to 9.6 percent.[2]
This overview was last updated in November 2023. Priority is given to the latest available official data published by national statistical offices and/or public institutions.
Sources:
[1] Central Statistical Bureau. 2023. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.csb.gov.kw/Default_EN [Accessed 07 November 2023].
[2] International Labor Organization. 2023. ILOstat. [ONLINE] Available at: https://ilostat.ilo.org/ [Accessed 23 September 2023].
[3] World Health Organization. 2023. Global Health Observatory Data. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.who.int/gho/database/en/ [Accessed 15 October 2023].
[4] United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). 2023. Human Development Index. [ONLINE] Available at: https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/documentation-and-downloads; https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/country-insights#/ranks [Accessed 25 October 2023]..
[5] The World Bank. 2019. Doing Business 2020. [ONLINE] Available at: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/688761571934946384/pdf/Doing-Business-2020-Comparing-Business-Regulation-in-190-Economies.pdf [Accessed 4 May 2020].
[6] Central Bank of Kuwait. 2023. The Economic Report for the year 2020 and previous reports. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.cbk.gov.kw/en/statistics-and-publication/publications/economic-reports [Accessed 07 November 2023].
[7] National Assembly. May 2018. Budget Committee: The government decided to postpone the application of VAT until 2021 and to expedite measures for excise tax on tobacco, energy and carbonated drinks. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.kna.kw/clt-html5/news-details.asp?id=30070 [Accessed 4 May 2020].
[8] International Monetary Fund. 2023. World Economic Outlook. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/SPROLLs/world-economic-outlook-databases#sort=%40imfdate%20descending [Accessed 24 October 2023].
Data Highlights
-
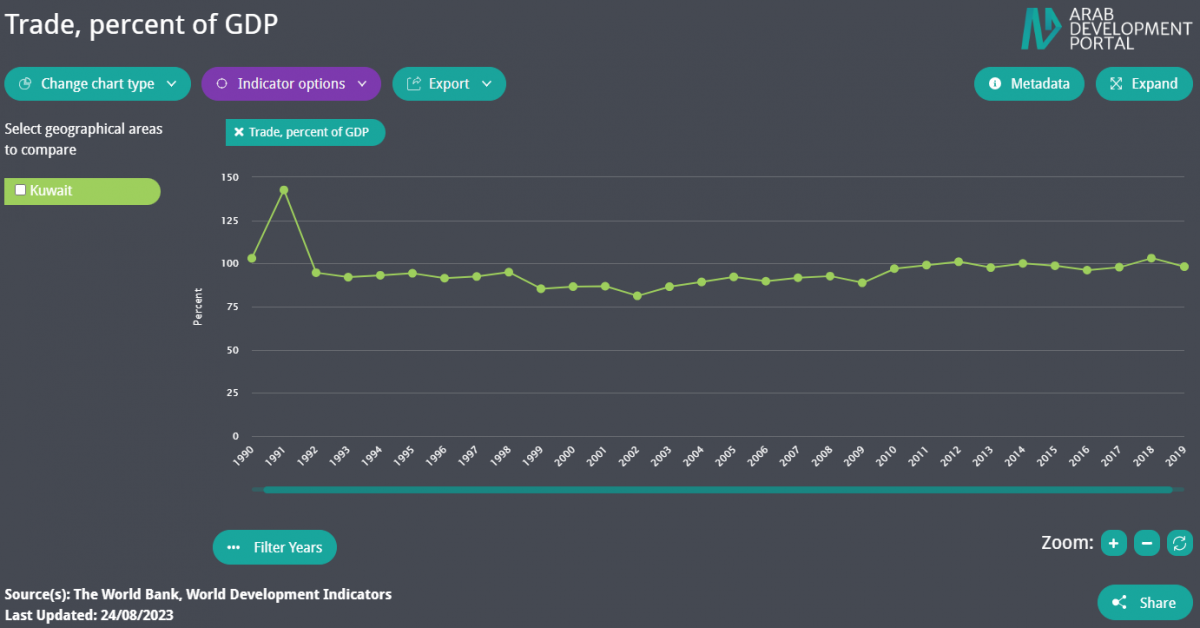
Trade has always had a significant weight in Kuwait’s economy, with the international trade-to-GDP ratio moderately increasing over the last 2 decades from 86.6% in 2000 to 98.1% in 2019.